QUARTZ F.A.Q.

Are there quartz movements with a smooth sweep second hand?
Yes. Seiko made a 5S21 calibre with a smooth sweeping hand back in the 90s. The stepper fires every 250ms, four times more often than the standard stepper motor. This impulse is fed through a spiral spring and into a damper system which feeds the pulse smoothly into the gear train to give the impression of a smooth continuous push from the stepper motor.
A similar design powers the current generation of smooth sweep clock movements from the Japanese.
There are also various chronograph modules from Seiko (e.g. the 7t62) and Citizen (e.g. the 2100) that have central chrono seconds ticking 5 times a second. Some ETA/Ronda quartz also have sub second hands that spin one revolution per second when the chronograph is activated.
The Seiko Spring drive is a quartz/mechanical hybrid with a true smooth sweep (i.e. no discrete steps).
Are there true-GMT quartz watches?
Yes. All Seiko GMT watches (mechanical, quartz/kinetic, spring drive) have true GMT function (i.e. the 12 hour hand (linked to the date) quicksets in 1 hour intervals forward and backward). The two quartz calibres still in production are the 8F56 and 5M65.
Citizen also makes/made several GMT watches that quicksets the 12 hour hand forward in 1 hr intervals.
The Swiss ETA and Ronda GMT movements quickset the 24 hour hand forward.
Can quartz watches be calibrated?
Most modern movements lack adjustment terminals, so the rate cannot be adjusted after they leave the factory. High end movements such as the thermoline ETAs and Seiko 9Fxx, 8Jxx can be rate adjusted with the proper equipment. ETAs can be adjusted at home by a knowledgable HEQ enthusiast as the manual is published by ETA. Citizen and Seiko maintain secrecy on adjustment rates so you will have to send it in for factory adjustment. The very tight specifications on accuracy performance maybe the reason Seiko and Citizen discourage home adjustments. Cutting the quartz will also adjust the frequency but such adjustments are permanent and not recommended unless it is done by the manufacturer.
Do spent batteries leak inside movements?
Modern silver oxide and lithium chemistry based cells rarely leak, even if left inside for a good number of years. One caveat: buy cells from reputable brands such as Panasonic, Renata, Seiko, Energizer etc.
How does a radio-controlled/atomic-sync watch work?
A radio controlled/atomic sync watch is a quartz watch that’s periodically reset (usually once a day between 12 a.m. to 6 a.m.) by radio signals received from one of six atomic clock transmitters worldwide. There are two in Japan, one in China, one in the U.S.A., one in the U.K. and one in Germany.
There are single band, dual band, five band and six band atomic-sync watches currently on market that’s able to sync with any one or all of the radio transmitters worldwide.
In the absence of atomic calibration, the watches are mostly rated to ±15s/month accuracy at normal temperatures (i.e. between 5 and 35 oC)
How does an analogue quartz watch work?
These are the typical components found in a single stepper quartz movement.

Image credit: Explainthatstuff.com
1. Battery.
2. Lavet type stepping motor, also commonly known as the coil.
3. Microchip.
4. IC connects microchip to other components.
5. Tuning fork shaped quartz crystal oscillator in sealed cylinder.
6. Stem connecting crown to clutch for time-setting.
7. Reduction gearing for minute and hour hands.
8. Tiny central shaft holds hands in place.
To illustrate how the various components work together to keep time, refer to the simplified layout below.

Image credit: FHS
The battery (1) provides power to the IC (2). The tuning fork shaped quartz crystal (3) in turn vibrates at a stable 32K hertz (32,768 vibrations per second) due to the piezoelectric effect. The trimmer (4) consist of capacitor(s) in series/parallel with the crystal. It regulates the resonant frequency of the tandem setup. This is fixed at the factory in modern movements. The resultant signal is counted by the IC in binary fashion such that the stepper (5) fires every 215 counts. This is the familiar one-second ticking seen in quartz watches. The gear train (6) powers the minute and hour hands (7) via reduction gearing.
How does one know the quality of the quartz movement in a specific watch?
Swiss watch MSRP is not a reliable indicator of the movement’s quality, because the movement used is usually not revealed. Take the Marathon TSAR, which is a $450 watch. It uses a ISA 1198 that costs $7 at retail. Tag Heuer is also known to stick ordinary ETA movements into many of their quartz models, when their MSRP deserve the exclusive use of the Flatline range, ETA’s premier non-thermocompensated movement range.
The cachet/cost hierarchy is approximately ISA<Ronda<ETA (all others)<ETA (Flatline)<ETA (Thermoline).
For Japanese watches, the movement used is always described on the caseback and manual. Price/quality correlates well.
How does the stepper motor work?

Image credit: Infolytica
This above is a typical lavet-type stepper. Every second, the coil is powered by current from the IC which induces a magnetic field around the coil, forcing the rotor to turn 180 degrees. The polarity of the coil is reversed the next time it fires (i.e. a 2-second periodic cycle).
How is high accuracy achieved in a quartz movement?
High accuracy, for the purpose of discussion, is accuracy bettering the 2001 COSC quartz chronometer standard of ~±25s/year. It is achieved using 1) high frequency thermoinsensitive crystal and 2) thermocompensation. Both methods flattens the effective temperature response curve of the crystal.
Thermocompensation (TC), as the term suggests, compensates for the shift in frequency of the quartz crystal as the temperature changes. This is accomplished in modern TC movements using a digital inhibition scheme that reads off the temperature via a separate thermistor on the movement. Some quartz movements uses higher frequency to achieve greater accuarcy. A good example are Seiko's 8FXX 196 KHz movement while some older Seiko used twin quartz compensation for greater accuracy. However, the single biggest enemy for quartz accuracy remains to be temperature fluctuations.
Is a quartz movement repairable?
Yes and no. Many modern movements are not designed to be repaired because it’s much cheaper to drop in a replacement module. However, even repairable movements are seldom touched by watchmakers because they either 1) don’t have the necessary equipment such as quartz watch timers, circuit/coil testers; 2) can’t make money off them; or 3) are just out of their depth when it comes to electrical engineering.
Is the capacitor in Seiko Kinetic movements problematic?
Modern Seiko kinetics at the under $500 range no longer use capacitors but lithium ion rechargeables with 1 month or more PR. These have been proven to be reliable unless run down and stored for a long time.
The problem capacitors were found on those 2001-2002 models with 7-14 day PR.
Should I pull out the crown if I’m not wearing my quartz watch?
In general no, unless the manual states otherwise. It is likely the circuit will consume more or equal power with the crown pulled out. However, many Ronda movements go into power-saving mode with the crown pulled out.
What is a fly-by-wire movement?
A movement without a direct crown-hand linkage. The most distinctive are the analogue four-button Casios. Citizen, Seiko and Junghans also have several analogue/ana-digi models. Such watches have the best hand/marker alignment due to a unique stepper design (multi-pole) and the absence of a setting clutch/gear train.
What is a kinetic/eco-drive/solar watch?
A quartz watch using a rechargeable power source (li-ion battery or capacitor) coupled to a charging mechanism. The kinetic uses a gravity activated weight to spin an ultrasonic generator while eco-drive/solar charge via solar panels on the dial.
What is a quartz chronometer?
The 2001 quartz chronometer standard passes movements certified over 11 days with the following spec:
1. Average daily rate at 23 °C: +/-0.07
2. Rate at 8 °C: +/-0.2
3. Rate at 38 °C: +/-0.2
4. Rate stability: 0.05
5. Dynamic rate: +/-0.05
6. Temporary effect of mechanical shocks +/-0.05
7. Residual effect of mechanical shocks +/-0.05, 200 shocks equivalent to 100 G (981 m/s²)
8. Rate resumption +/-0.05
Measurements are based on a time base established by two independent atomic clocks synchronised on GPS time.
What is the accuracy of a Citizen Campanola?
±20s/month. The selling point is dial work, finishing and first rate appearance. The opulence of mechanical watches with quartz accuracy. All Campanola are either hand made or hand finished and the movements are hand assembled. Their real life accuracy usually surpassed the conservative claims as evident in Seiko's Spring Drive's performance as well.
What is the battery life on a typical quartz movement?
>2 years. Some movements powered by lithium cells are rated to 10 years.
What is the life expectancy of a typical analogue quartz watch?
A well maintained (watertight gaskets, oiled, regular battery change) non-abused quartz watch should last at least 10-20 years. Many quartz watches from the 70s still survive today. Grand Seiko 9Fxx movements are vacuum sealed and guaranteed to >50 years between service intervals.
What is the purpose of hi-torque movements found in dive watches?
Provide excess power to drive heavy lumed hands reliably in conditions of shock and low-temperature (where the voltage supplied by the cell decreases due to a slowdown in the chemistry).
What is the purpose of jewels in a quartz watch?
Found usually only on quality quartz movements, they reduce wear and tear of the gear/date train. It is doubtful they are necessary since the major component failure lie in the stepper.
What is the typical accuracy of a quartz watch?
No better than ±15s/month or thereabouts for 99.99% of all quartz watches between $5 and $5’000. And yes, that includes every single quartz Tag Heuer ever made, every Omega other than the Double Eagle, every modern Longines/Concord/insert non-Breitling Swiss quartz watch.
Some cheap quartz watches are rated to ±30 or worse.
The number of high-accuracy timepieces with accuracy better than ±25s/year is very limited.
What should I do if the second hand starts to jump at intervals other than one second?
Replace the battery. This is the EOL indicator.
When was the first quartz timepiece developed? The first watch?
The first use of quartz technology to track time occured in 1923, and in 1927 Warren Marrison and J.W. Horton built the first quartz clock at Bell Telephone Laboratories. The first quartz watch was the Seiko Astron introduced on Christmas day 1969. The first mass produced quartz movement was the Swiss CEH Beta 21 introduced in early 1970.
Which are the brands offering radio-controlled/atomic-sync lines?
Casio, Citizen, Seiko, Junghans.
Which are the major quartz movement suppliers?
Swiss: ISA, Ronda, ETA
Japanese: Seiko, Citizen/Miyota, Casio
Others: Timex
Which are the thermocompensated high-end quartz lines currently on market?
Breitling (all Superquartz models), Sinn (UX), Omega (Constellation Double Eagle), Seiko (Dolce & Exceline, Grand Seiko, Credor, M, Brightz), Citizen (Exceed, Chronomaster)
Which type of movement have well aligned second hand to marker characteristics?
Fly-by wire movements without a setting clutch. The Grand Seiko 9FXX movement employs the double bounce method for the second hand to track the markers more accurately.
Why is the second hand not aligned with the markers all around the dial?
Gear/stepper slack/tolerance is the main culprit. It has little to do with dial/center pinion misalignment/misprint. If the hand is misaligned consistently around the dial, a hand reset by the watchmaker will solve the problem.

Are there quartz movements with a smooth sweep second hand?
Yes. Seiko made a 5S21 calibre with a smooth sweeping hand back in the 90s. The stepper fires every 250ms, four times more often than the standard stepper motor. This impulse is fed through a spiral spring and into a damper system which feeds the pulse smoothly into the gear train to give the impression of a smooth continuous push from the stepper motor.
A similar design powers the current generation of smooth sweep clock movements from the Japanese.
There are also various chronograph modules from Seiko (e.g. the 7t62) and Citizen (e.g. the 2100) that have central chrono seconds ticking 5 times a second. Some ETA/Ronda quartz also have sub second hands that spin one revolution per second when the chronograph is activated.
The Seiko Spring drive is a quartz/mechanical hybrid with a true smooth sweep (i.e. no discrete steps).
Are there true-GMT quartz watches?
Yes. All Seiko GMT watches (mechanical, quartz/kinetic, spring drive) have true GMT function (i.e. the 12 hour hand (linked to the date) quicksets in 1 hour intervals forward and backward). The two quartz calibres still in production are the 8F56 and 5M65.
Citizen also makes/made several GMT watches that quicksets the 12 hour hand forward in 1 hr intervals.
The Swiss ETA and Ronda GMT movements quickset the 24 hour hand forward.
Can quartz watches be calibrated?
Most modern movements lack adjustment terminals, so the rate cannot be adjusted after they leave the factory. High end movements such as the thermoline ETAs and Seiko 9Fxx, 8Jxx can be rate adjusted with the proper equipment. ETAs can be adjusted at home by a knowledgable HEQ enthusiast as the manual is published by ETA. Citizen and Seiko maintain secrecy on adjustment rates so you will have to send it in for factory adjustment. The very tight specifications on accuracy performance maybe the reason Seiko and Citizen discourage home adjustments. Cutting the quartz will also adjust the frequency but such adjustments are permanent and not recommended unless it is done by the manufacturer.
Do spent batteries leak inside movements?
Modern silver oxide and lithium chemistry based cells rarely leak, even if left inside for a good number of years. One caveat: buy cells from reputable brands such as Panasonic, Renata, Seiko, Energizer etc.
How does a radio-controlled/atomic-sync watch work?
A radio controlled/atomic sync watch is a quartz watch that’s periodically reset (usually once a day between 12 a.m. to 6 a.m.) by radio signals received from one of six atomic clock transmitters worldwide. There are two in Japan, one in China, one in the U.S.A., one in the U.K. and one in Germany.
There are single band, dual band, five band and six band atomic-sync watches currently on market that’s able to sync with any one or all of the radio transmitters worldwide.
In the absence of atomic calibration, the watches are mostly rated to ±15s/month accuracy at normal temperatures (i.e. between 5 and 35 oC)
How does an analogue quartz watch work?
These are the typical components found in a single stepper quartz movement.

Image credit: Explainthatstuff.com
1. Battery.
2. Lavet type stepping motor, also commonly known as the coil.
3. Microchip.
4. IC connects microchip to other components.
5. Tuning fork shaped quartz crystal oscillator in sealed cylinder.
6. Stem connecting crown to clutch for time-setting.
7. Reduction gearing for minute and hour hands.
8. Tiny central shaft holds hands in place.
To illustrate how the various components work together to keep time, refer to the simplified layout below.
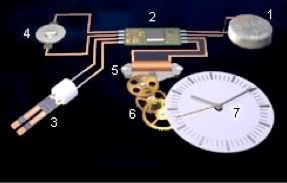
Image credit: FHS
The battery (1) provides power to the IC (2). The tuning fork shaped quartz crystal (3) in turn vibrates at a stable 32K hertz (32,768 vibrations per second) due to the piezoelectric effect. The trimmer (4) consist of capacitor(s) in series/parallel with the crystal. It regulates the resonant frequency of the tandem setup. This is fixed at the factory in modern movements. The resultant signal is counted by the IC in binary fashion such that the stepper (5) fires every 215 counts. This is the familiar one-second ticking seen in quartz watches. The gear train (6) powers the minute and hour hands (7) via reduction gearing.
How does one know the quality of the quartz movement in a specific watch?
Swiss watch MSRP is not a reliable indicator of the movement’s quality, because the movement used is usually not revealed. Take the Marathon TSAR, which is a $450 watch. It uses a ISA 1198 that costs $7 at retail. Tag Heuer is also known to stick ordinary ETA movements into many of their quartz models, when their MSRP deserve the exclusive use of the Flatline range, ETA’s premier non-thermocompensated movement range.
The cachet/cost hierarchy is approximately ISA<Ronda<ETA (all others)<ETA (Flatline)<ETA (Thermoline).
For Japanese watches, the movement used is always described on the caseback and manual. Price/quality correlates well.
How does the stepper motor work?
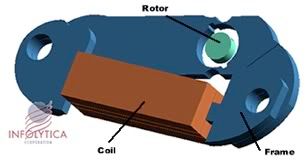
Image credit: Infolytica
This above is a typical lavet-type stepper. Every second, the coil is powered by current from the IC which induces a magnetic field around the coil, forcing the rotor to turn 180 degrees. The polarity of the coil is reversed the next time it fires (i.e. a 2-second periodic cycle).
How is high accuracy achieved in a quartz movement?
High accuracy, for the purpose of discussion, is accuracy bettering the 2001 COSC quartz chronometer standard of ~±25s/year. It is achieved using 1) high frequency thermoinsensitive crystal and 2) thermocompensation. Both methods flattens the effective temperature response curve of the crystal.
Thermocompensation (TC), as the term suggests, compensates for the shift in frequency of the quartz crystal as the temperature changes. This is accomplished in modern TC movements using a digital inhibition scheme that reads off the temperature via a separate thermistor on the movement. Some quartz movements uses higher frequency to achieve greater accuarcy. A good example are Seiko's 8FXX 196 KHz movement while some older Seiko used twin quartz compensation for greater accuracy. However, the single biggest enemy for quartz accuracy remains to be temperature fluctuations.
Is a quartz movement repairable?
Yes and no. Many modern movements are not designed to be repaired because it’s much cheaper to drop in a replacement module. However, even repairable movements are seldom touched by watchmakers because they either 1) don’t have the necessary equipment such as quartz watch timers, circuit/coil testers; 2) can’t make money off them; or 3) are just out of their depth when it comes to electrical engineering.
Is the capacitor in Seiko Kinetic movements problematic?
Modern Seiko kinetics at the under $500 range no longer use capacitors but lithium ion rechargeables with 1 month or more PR. These have been proven to be reliable unless run down and stored for a long time.
The problem capacitors were found on those 2001-2002 models with 7-14 day PR.
Should I pull out the crown if I’m not wearing my quartz watch?
In general no, unless the manual states otherwise. It is likely the circuit will consume more or equal power with the crown pulled out. However, many Ronda movements go into power-saving mode with the crown pulled out.
What is a fly-by-wire movement?
A movement without a direct crown-hand linkage. The most distinctive are the analogue four-button Casios. Citizen, Seiko and Junghans also have several analogue/ana-digi models. Such watches have the best hand/marker alignment due to a unique stepper design (multi-pole) and the absence of a setting clutch/gear train.
What is a kinetic/eco-drive/solar watch?
A quartz watch using a rechargeable power source (li-ion battery or capacitor) coupled to a charging mechanism. The kinetic uses a gravity activated weight to spin an ultrasonic generator while eco-drive/solar charge via solar panels on the dial.
What is a quartz chronometer?
The 2001 quartz chronometer standard passes movements certified over 11 days with the following spec:
1. Average daily rate at 23 °C: +/-0.07
2. Rate at 8 °C: +/-0.2
3. Rate at 38 °C: +/-0.2
4. Rate stability: 0.05
5. Dynamic rate: +/-0.05
6. Temporary effect of mechanical shocks +/-0.05
7. Residual effect of mechanical shocks +/-0.05, 200 shocks equivalent to 100 G (981 m/s²)
8. Rate resumption +/-0.05
Measurements are based on a time base established by two independent atomic clocks synchronised on GPS time.
What is the accuracy of a Citizen Campanola?
±20s/month. The selling point is dial work, finishing and first rate appearance. The opulence of mechanical watches with quartz accuracy. All Campanola are either hand made or hand finished and the movements are hand assembled. Their real life accuracy usually surpassed the conservative claims as evident in Seiko's Spring Drive's performance as well.
What is the battery life on a typical quartz movement?
>2 years. Some movements powered by lithium cells are rated to 10 years.
What is the life expectancy of a typical analogue quartz watch?
A well maintained (watertight gaskets, oiled, regular battery change) non-abused quartz watch should last at least 10-20 years. Many quartz watches from the 70s still survive today. Grand Seiko 9Fxx movements are vacuum sealed and guaranteed to >50 years between service intervals.
What is the purpose of hi-torque movements found in dive watches?
Provide excess power to drive heavy lumed hands reliably in conditions of shock and low-temperature (where the voltage supplied by the cell decreases due to a slowdown in the chemistry).
What is the purpose of jewels in a quartz watch?
Found usually only on quality quartz movements, they reduce wear and tear of the gear/date train. It is doubtful they are necessary since the major component failure lie in the stepper.
What is the typical accuracy of a quartz watch?
No better than ±15s/month or thereabouts for 99.99% of all quartz watches between $5 and $5’000. And yes, that includes every single quartz Tag Heuer ever made, every Omega other than the Double Eagle, every modern Longines/Concord/insert non-Breitling Swiss quartz watch.
Some cheap quartz watches are rated to ±30 or worse.
The number of high-accuracy timepieces with accuracy better than ±25s/year is very limited.
What should I do if the second hand starts to jump at intervals other than one second?
Replace the battery. This is the EOL indicator.
When was the first quartz timepiece developed? The first watch?
The first use of quartz technology to track time occured in 1923, and in 1927 Warren Marrison and J.W. Horton built the first quartz clock at Bell Telephone Laboratories. The first quartz watch was the Seiko Astron introduced on Christmas day 1969. The first mass produced quartz movement was the Swiss CEH Beta 21 introduced in early 1970.
Which are the brands offering radio-controlled/atomic-sync lines?
Casio, Citizen, Seiko, Junghans.
Which are the major quartz movement suppliers?
Swiss: ISA, Ronda, ETA
Japanese: Seiko, Citizen/Miyota, Casio
Others: Timex
Which are the thermocompensated high-end quartz lines currently on market?
Breitling (all Superquartz models), Sinn (UX), Omega (Constellation Double Eagle), Seiko (Dolce & Exceline, Grand Seiko, Credor, M, Brightz), Citizen (Exceed, Chronomaster)
Which type of movement have well aligned second hand to marker characteristics?
Fly-by wire movements without a setting clutch. The Grand Seiko 9FXX movement employs the double bounce method for the second hand to track the markers more accurately.
Why is the second hand not aligned with the markers all around the dial?
Gear/stepper slack/tolerance is the main culprit. It has little to do with dial/center pinion misalignment/misprint. If the hand is misaligned consistently around the dial, a hand reset by the watchmaker will solve the problem.









