Work smart, not hard. We utilize the power of cloud AI platforms from Google, Microsoft, Amazon, IBM and Clarifai in under 15 minutes. For tasks not solved with existing APIs, we then use custom classification services to train classifiers without coding. And then we pit them against each other in an open benchmark, you might be surprised who won. Read online here.
Below, we present the graphical summaries of experiments conducted in chapter 8. For detailed experimental methodology for each experiment, refer to the text in Chapter 8 visible here. To reproduce the benchmarks please refer to the instructions.
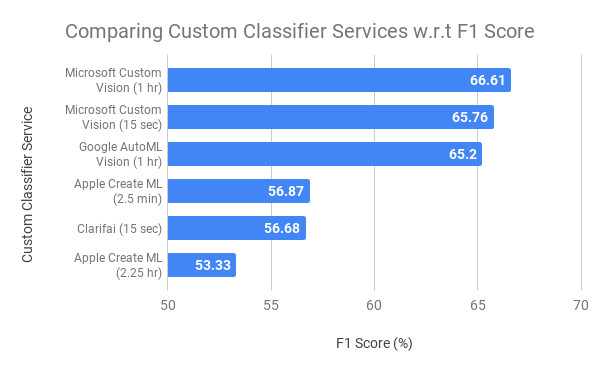
Comparing F1 score for custom classifier services, as of August 2019 (higher is better)
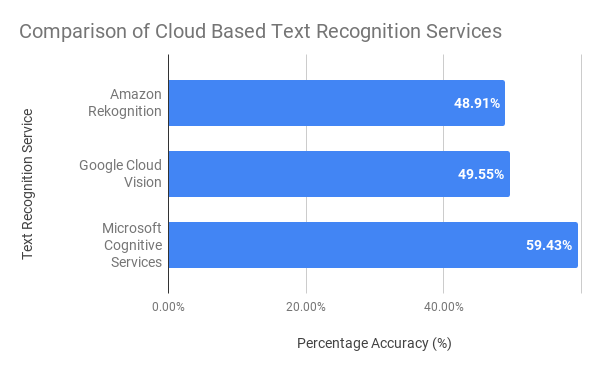
Word Error Rate for different text extraction APIs, as of August 2019 You can run this benchmark following the instructions.
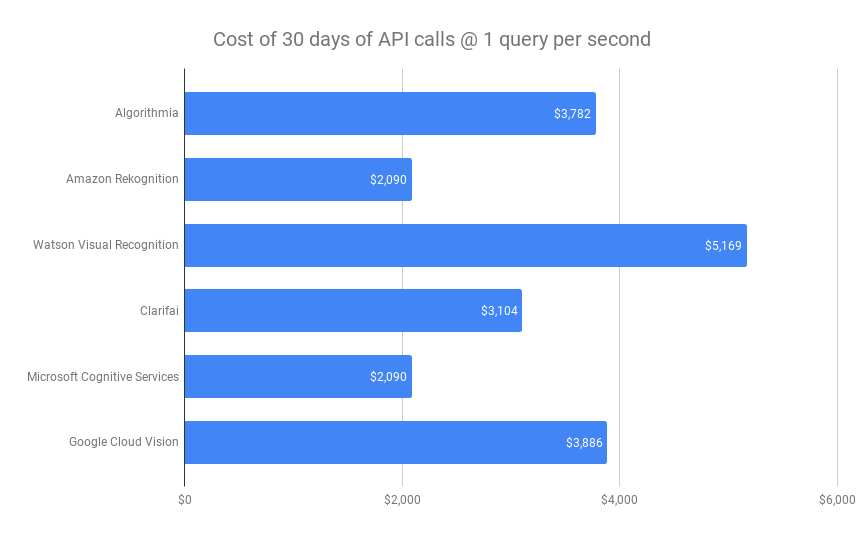
Cost comparison of different cloud-based vision APIs
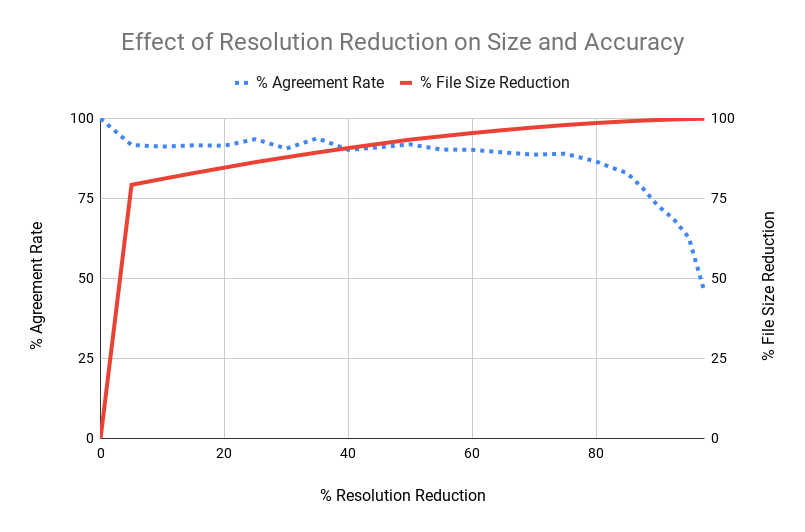
Effect of resizing an image on agreement rate and file size reduction relative to the original image
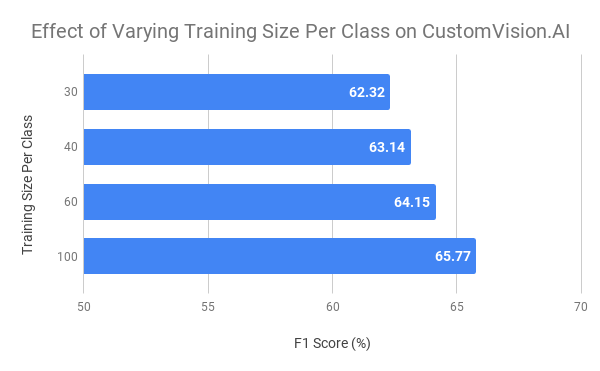
Effect of varying size of training data per class on test F1 score (higher is better)
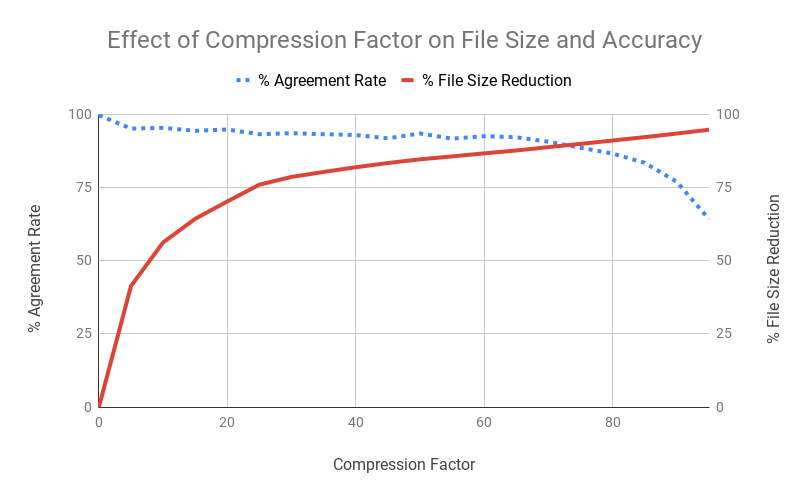
Effect of compressing an image on agreement rate and file size reduction relative to the original image
Comparison shopping of vision API providers (as of Aug 2019)
Examining services offered by each cloud provider.
| Algorithmia | Amazon Rekognition | Clarifai | Microsoft Cognitive Services | Google Cloud Vision | IBM Watson Visual Recognition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image classification | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Image detection | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| OCR | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Face recognition | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Emotion recognition | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Logo recognition | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Landmark recognition | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Celebrity recognition | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Multi-lingual tagging | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Image description | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Handwriting | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Thumbnail generation | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Content - moderation | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Custom classification training | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Custom detector training | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Mobile custom models | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Free tier | 5,000 requests per month | 5,000 requests per month | 5,000 requests per month | 5,000 requests per month | 1,000 requests per month | 7,500 |
In this chapter, we will be going through two experiments of image tagging or object recognition, and optical character recognition (OCR). Image tagging helps us understand what objects are present inside an image. OCR helps decipher the characters present in an image. We will be uploading images from the MSCOCO dataset to various cloud providers and comparing the results.
We will be using the Google, Microsoft, and Amazon cloud providers to test for image tagging and optical character recognition. Please sure you register and generate an API key for each and replace it in the respective scripts in the experiment-scripts directory.
-
1-get-MSCOCO-validation-image-ids-with-legible-text.ipynb: We will develop a dataset of images from the MSCOCO dataset that contain at least a single instance of legible text and are in the validation split.
-
2-test-ocr-from-cloud-providers.ipynb:This code sample details how one image and a directory of images can be uploaded to various cloud providers using the scripts in
experiment-scripts. We will be using separate scripts for both the OCR and image tagging experiments. -
3-upload-validation-images-to-cloud-providers.ipynb: In this file we will gather the data that enables us to do the benchmarking.
-
4-compile-ground-truth-ocr.ipynb: In this file we will compile the ground truth for all the test images.
-
5-compile-results-ocr.ipynb: In this file we will compile the results using the ground truth and the collected data for all the test images. Each cloud provider sends the results in slightly different formats and we need to parse each of them correctly. So, we will develop a parsing function unique to each cloud provider in this file as well.
-
1-setup.ipynb: Compile the intermediate files that we need for the benchmarking.
-
2-compile-ground-truth-tags.ipynb: Compile the ground truth for all the test images.
-
3-upload-validation-images-to-cloud-providers.ipynb: Gather the data that enables us to do the benchmarking. We will be using the Google, Microsoft, and Amazon cloud providers
-
4-compile-results-tags.ipynb: Compile the final results by comparing ground truth against the received predictions.
Please download both the MSCOCO images, available on the MSCOCO project website. To make experimentation seamless, we have also provided the predictions obtained from our runs in August 2019 in the data-nov-2019 directory.
We will be using the COCO-Text dataset for Optical Character Recognition. We will utilize its Python API for loading and parsing the annotations. More information on the COCO-Text dataset is available on its website. Please download the API. The various files that we will be utilizing from COCO-Text are:
cocotext.v2.json: Please download this file and update the path in the corresponding notebooks.coco_evaluation.pycoco_text.py: This file is being imported in various notebooks. Please make sure that this file is available in the same folder as the notebooks.
Please download the text annotations from the coco-text website.
Please download Gensim, which we will be using for comparing word similarity between ground truth with predicted class. The paths to the GoogleNews-vectors-negative300.bin will need to be updated in the corresponding notebooks.